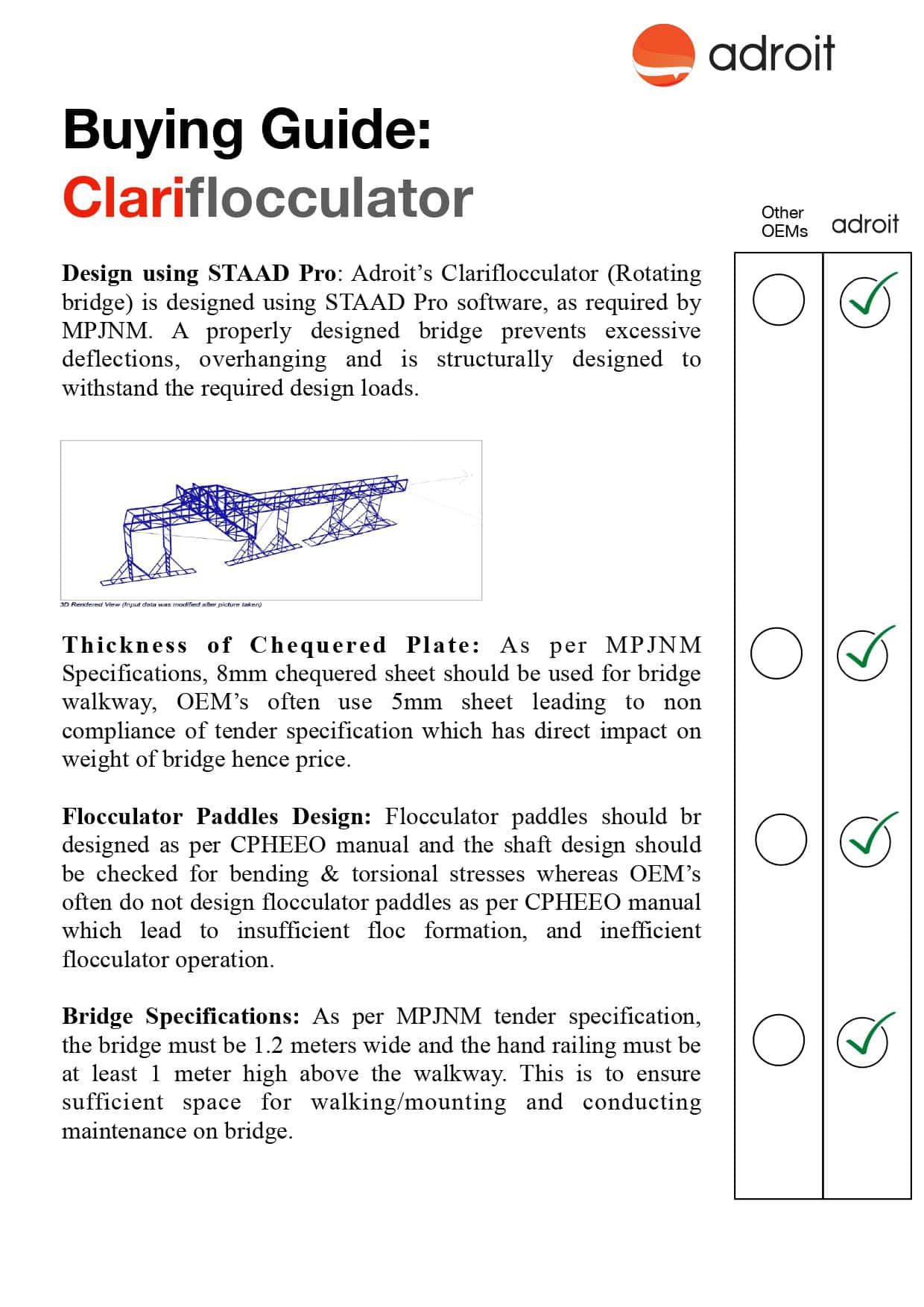
Industrial agitator is a crucial part in Industries for effective mixing, energy efficiency, and longevity of equipment. Adroit understands the significance of a perfectly chosen agitator. They play a vital role in multiple industries like chemical processing, wastewater treatment, pharmaceuticals, and food production. A perfect agitator ensures thriving processes by performing preferred mixing results while preserving energy. Here we shared information about calculating the Agitator Power and Understanding Design & Requirements for Optimal Mixing Performance.
Calculating Agitator Power and Understanding Design & Requirements for Optimal Mixing Performance
Understanding Agitator and Mixer Design
Agitators have the property of different designs suitable for different applications. Their structure involves a detailed review of many aspects, such as:
- Types of Impeller: Different shapes of impellers control the mixing flow and efficiency for different tasks, like axial, radial, and tangential.
- Tank Geometry: The tank’s shape and qualities, such as baffles, influence how well the agitator combines fluids, controlling areas with bad circulation.
- Mixing Goals: Different procedures need different agitator structures for applications like blending, emulsification, or gas dispersion.
- Power and Torque Requirements: This requirement is to be calculated as per fluid properties and functioning conditions to ensure energy efficiency and prolong the life of the equipment.
Agitator Power Calculation: Formula and Factors
Calculating the power required for an agitator is crucial for sizing the motor perfectly and ensuring efficient energy consumption. The most common formula for this calculation is:
P = Np × ρ × N³ × D⁵
Explanation:
- P = Power Needed (Watts or kW
- Np = Power number (dimensionless, impeller-dependent
- ρ = Fluid density (kg/m³
- N = Rotational speed (revolutions per second or per minute
- D = Impeller diameter (m)
The Power Number (Np) depends on the kind of impeller operated. For example, propellers have lower Np values, while high-shear impellers, such as Rushton turbines, have higher values. This equation is key for deciding the motor size required for the usage, helping the agitator run perfectly while minimizing energy usage.
Buyer’s Guide: Choosing the Right Industrial Agitator
When selecting an agitator, it is very crucial to evaluate multiple factors to ensure the most suitable fit for your task. Here are some major points to asses:
Mixing Objectives
Many mixing purposes need different types of impeller designs:
- Homogenization: Axial-flow impellers like hydrofoils or marine propellers are suitable for boosting flow along the shaft.
- Solid Suspension: Axial or pitched-blade turbines are ideal for keeping solids in suspension.
- Gas Dispersion: Radial-flow impellers like Rushton turbines are beneficial for mixing gas and liquid.
- Heat Transfer: High-turbulence structures are favorable for efficient heat transfer.
Fluid Properties
The fluid elements are important for choosing the perfect agitator:
- Low-Viscosity Fluids: Axial-flow propellers are more suitable as they form efficient flow with low shear.
- Medium-Viscosity Fluids: Pitched-blade turbines deliver an ideal balance of shear and flow.
- High-Viscosity Fluids: Anchor or helical ribbon agitators are required to blend thick materials perfectly.
Tank Configuration
Tank design is crucial for deciding on an agitator:
- Baffles: Baffles control vortexing and improve upright mixing, ensuring the entire liquid volume is mixed correctly.
- Tall Tanks: Multi-stage impellers are usually required in tall tanks to gain complete fluid turnover and provide lively mixing while dodging short-circuiting.
Energy Efficiency & Maintenance
To lower operational costs and enhance the lifespan of the agitator system:
- Variable Frequency Drives: These optimize speed to lower power consumption and allow for adjustments as per the requirements of the procedure.
- Material & Sealing: Use stainless steel or coated impellers for corrosive fluids, and select mechanical seals for uses with pressure situations.
Types of Agitator Designs
The selection of agitator design depends on the type of procedure being carried out. Here are some typical designs:
Impellers
- Axial-Flow Impellers: These impellers form a flow along the shaft’s axis, making them perfect for mixing and suspending materials.
- Radial-Flow Impellers: They generate shear forces, making them correct for gas-liquid blending or extreme mixing requirements.
Paddles
Paddles function at low speeds and are suitable for high-viscosity fluids. These are usually utilized in industries such as pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and polymers, requiring mild but effective mixing.
Propellers
Propellers are efficient, low-shear mixers typically utilized in water treatment plants for large-volume mixing. They are developed for medium flow rates with minimal shear strain.
How to Optimize Agitator Performance?
Here we mentioned the key aspects to optimize the efficiency and longevity of the agitator system:
Choose the Right Impeller Size: A Larger impeller works better at lower speeds and saves energy to provide effective mixing.
Fine-Tune Speeds with a VFD: The use of varying speed control optimizes the agitator’s working and controls the cavitation.
Use CFD Simulations: Computational Fluid Dynamics simulations support indicating mixing manners and deciding possible issues before making the equipment.
Consider Impeller Positioning: Off-center impeller positioning can improve circulation, particularly in unbaffled tanks where mixing might be irregular.
What are the Common Challenges in Agitator Design?
The design of Agitator plays a crucial role in achieving consistent and efficient mixing, but there are several common challenges in Agitator design, including:
- Power mismatch: A frequent problem is choosing the wrong power size. An agitator that is undersized for the application will not behave in the manner required, and solids will settle out. An oversized agitator is expensive and wastes extra energy unnecessarily, increasing the operator’s costs.
- Settling and dead zones: When the impeller is poorly positioned in the tank or is poorly designed for the tank geometry, it will often cause solids to settle. Poor agitation leads to poor mixing performance and poor through-put which negatively impacts overall treatment.
- Poor gas distribution: When aerating, the purpose is to disperse oxygen. If the agitator is a weak design, gas transfer will not be effective and biological reactions will slow down during wastewater treatment.
- Wear and corrosion of materials: Wastewater has harsh conditions (e.g. abrasive solids, harsh chemicals) that can wear away impellers, shafts, and bearings should they not be made with the appropriate materials used for construction.
- Balancing shear forces: Sometimes you want vigorous agitation to break down solids, while other times you do not want to agitate intensely and allow floccule formation. Achieving balance is sometimes tricky.
- Maintenance: When designing an agitator, if the system does not allow access to check routine service, inspection or repairs, then labor and downtime will increase.
- Scaling up: Designs that work in a lab scale or pilot plant may not work in a large wastewater plant, as scaling remains a major stumbling block.
Why Choose Adroit for Agitator Solutions?
Adroit is a bunch of passionate engineers and experts seeking to transform the world of water via creative and reliable solutions. We specialize in custom-made engineered agitators, designed to manage the precise applications. Even if for wastewater treatment or mixing complicated pharmaceuticals, our services are the top choice across India and the Middle East.
Conclusion
In conclusion, selecting a suitable agitator is required for efficient mixing, energy conservation, and the durability of machinery. By evaluating aspects such as impeller types and tank design, you can make a perfect conclusion for your application. Adroit offers custom-made agitators to fulfill your unique needs of different industries.
FAQS for Calculating Agitator Power and Understanding Design & Requirements for Optimal Mixing Performance
Question 1. What materials are advisable for corrosive fluids agitators?
Answer: It is suggested to use stainless steel or coated impellers and mechanical seals for corrosive fluids. They can resist high-pressure conditions easily.
Question 2. How can we optimize the performance of our agitator?
Answer: For optimizing the performance of an agitator, choose the perfect size of impeller, use VFDs for speed control, execute CFDx to indicate mixing behavior, and evaluate impeller placement.
Question 3. Why should we choose Adroit for our agitator requirements?
Answer: Adroit is a leading company based in India, specializing in personalized agitators developed to fulfill unique procedures demand. Our solutions are popularly known for their longevity, accuracy, and high performance.
Question 4. What factors influence agitator design and power requirements?
Answer. There are several factors that influence agitator design and power requirements including:
Fluid properties (viscosity, density and solid content)
Mixing goals (blending, dispersion, suspension)
Tank geometry (size, shape and baffles)
Equipment factors like impeller type and speed
Question 5. How do you calculate agitator power for mixing applications?
Answer. Agitator power for mixing applications can be calculated using the Power Number Formula, which is P = Np × ρ × N³ × D⁵
Where,
Np is Power Number
ρ is the density of the fluid
N is the rotational speed of agitator
And D is the impeller diameter
Question 6. What are the common problems caused by incorrect agitator design?
Answer. Common problems that can be caused by incorrect agitator design include a wide range of process inefficiencies and mechanical failures, such as poor mixing, high energy consumption, equipment damage and serious safety hazards.
Question 7. How can I improve the energy efficiency of my agitator system?
Answer. By using energy efficient motors and variable frequency drives (VFDs), selecting the correct agitator size and impeller for the application, maintaining the system regularly to reduce friction and considering impeller designs can improve the energy efficiency of your agitator.