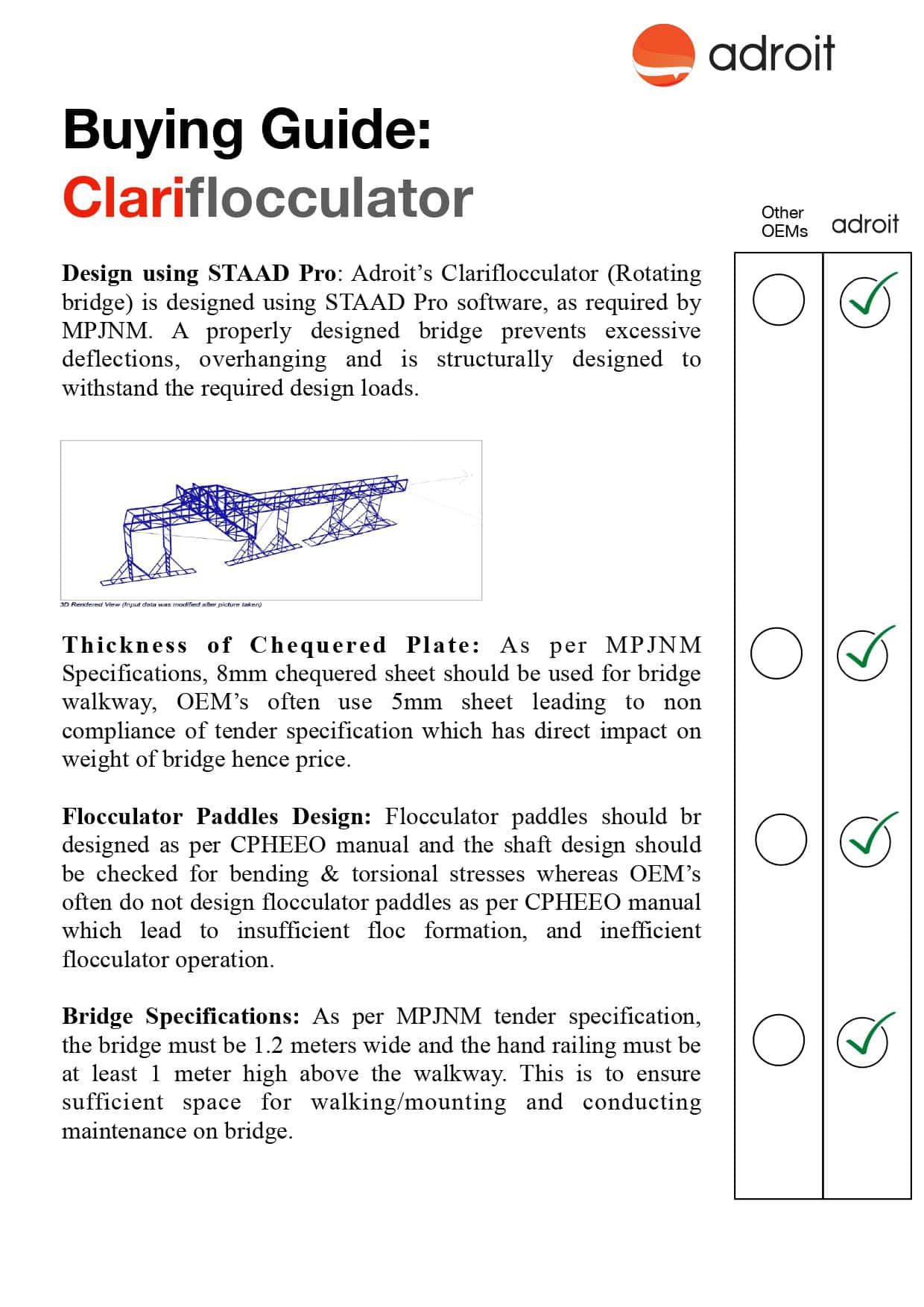
A guide for “What is a Sluice Gate? How It Works and Its Applications”. Sluice gates are essential components for water management and wastewater treatment. These gates serve as movable barriers that help control the water flow and level in different systems. Acting as the valve for waterways, these gates enable engineers to regulate water flow for multiple purposes. These structures are combined into the designs of rivers, dams, and irrigation purposes. Sluice gates are constructed with durable materials that can handle the large amount of water pressure. These gates are designed to handle the mechanism to raise or lower the gate to pass the water through it.
The main focus and function of these sluice gates is to manage the water resources. These types of systems can manage a wide range of applications, including the regulation of water supply for agricultural purposes, to control the water level for irrigation. These gates can protect the residents from floods, provide efficient irrigation, and maintain the balance of the ecosystem for aquatic life. The effectiveness of this system can offer significant water management practices across the world.
What is a Sluice Gate? How It Works and Its Applications
Breakdown of a sluice gate | Components
Sluice gates are the structures used to control the water flow and treatment of wastewater in different areas, including irrigation and flood control. These designs can vary depending on the size of the sluice gate, and the necessary components of the sluice gate may include:
- The gate is the main component of the system that moves and opens or closes the flow of water. These gates are made with durable materials that can withstand the amount of water. The shape of the gate (flat, radial, and wedge) can vary depending on the size and application.
- A frame is the structure that supports the gate and offers the guides with which the gate can move. It can be anchored to the concrete structure. sluice gate
- Sealing components are important for preventing leaks and may involve bronze or rubber that can seat faces on the gate and frame. The fixed sealing arrangement can ensure that the seal is tight when the gate is closed.
How does a sluice gate work?
A works mechanically to control water flow by opening in the river or any other waterway. The basic principle of the sluice gate is to create a movable barrier to pass the water flow. It works by lowering or raising the gate to allow the water to pass through it.
The sluice gate can be installed within the fixed frame, which defines the opening for water flow when the gate is open.
A movable disc or barrier is designed to slide vertically in the frame.
Sealing can prevent leakage when the gate is closed and creates a tight contact between the gate and frame.
Operating Mechanism:
The operating mechanism is used for raising or lowering the gate. Different components of the drive or operating mechanism include:
- A sluice gate can be hand-operated (via handwheel, chain, or worm drive).
- The sluice gate can be operated mechanically by using gears or screws.
- Hydraulic cylinders are used for the movement of the gate.
- Some sluice gates can be operated by electric motors to offer power for the mechanism.
- Flap sluice gates are systems that can operate automatically depending on the pressure.
- Wedges are the components that can ensure that the gate and seating faces of the frame are tightened. These components are to ensure tightness when the gate is in the closed position.
- The stem nut can convert the rotational motion of the stem into vertical movement of the gate.
Control of Water Flow
- When the gate is raised by the operating mechanism, it creates an opening through which the water flows. It works on the principle that if the gate is raised higher, the opening will be larger and the flow rate of water will be greater.
- When the gate is lowered by the gate, the size of the opening is reduced and the water flow is restricted. If the gate is lowered fully, it can block the water flow by sealing the frame.
- Sluice gates can be set the positions that can achieve the desired water flow rate and can maintain the required water flow.
How are sluice gates classified?
A sluice gate is a reliable device that controls the flow of water, which makes it an important component in water management systems and wastewater treatment. Different types of sluice gates are used in water management systems, depending on the design, purpose, and operation. The common classification for a sluice gate includes:
Depending on the Design/Movement of the Gates:
Vertical Lift Gates are the most common type of gate, depending on the design and movement. These gates can be flat or wedge-shaped plates that can slide vertically within a fixed frame. Vertical lift gates can be operated in different ways, including electrically, manually, or hydraulically.
- A rectangular or square plate is a flat sluice gate, which is a subtype of vertical lift gates.
- Wedge gates can create a tighter seal and are a type of vertical lift gate.
- Radial gates can have curved faces.
- Sector gates are similar to radial gates and are used in different applications, including irrigation and hydropower.
- Flap Gates are the type of gates that can be opened automatically due to the excessive water pressure.
- Stop Log Gates are manually placed into grooves that can create a temporary barrier.
Depending On Purpose/Application:
- Intake Sluice Gates are used to control the water flow into the system, which is located at the beginning of the irrigation channels or banks of the rivers.
- Control Sluice Gates can regulate the water levels and flow within the system.
- Divide Sluice Gates are used to break the flow of water.
- Drain Sluice Gates are the gates that can allow a two-way flow when required.
- Sluicing Gates are designed to flush the water from channels in emergencies.
- Rinse Sand Sluice Gates are designed to release water and are built at the end of sedimentation.
Based on Mounting Configuration:
- Channel-Mounted Sluice Gates are installed in the existing channel to offer support.
- Embedded Sluice gates can provide a strong and durable installation and incorporated into the surrounding structure.
- Flange-Mounted Sluice Gates allow the bolted flange connections to attach. The gates allow the attachment to the pipelines, which is common in the pressurised systems.
- Wall-mounted sluice gates are directly installed onto the concrete wall to save space.
What are the applications of sluice gates?
- Sluice gates are used in irrigation systems for water distribution, flow regulation, and water level control. These gates are used in the irrigation networks to control the excessive amount of water to ensure the efficient distribution of water to different areas.
- Sluice gates play an essential role in flood control and disaster management. For heavy rainfall, these gates can be opened to prevent flooding in areas with high populations.
- These gates play an important role in the generation of hydroelectric power. They can maintain the accurate level of water in dams that are efficient for power generation.
- In wastewater treatment plants and sewage systems, the sluice gates are used for flow regulation and management of the flow of sludge in the treatment procedures.
- Sluice gates have a significant application in industrial settings. For industrial applications, the sluice gates can be used for process control, tank isolation, and management of industrial effluents.
- In navigation, these gates can operate to control the water levels and regulate them water levels to maintain navigable depths.
- For environmental conservation, these gates can be used to control the water levels that can preserve and protect ecosystems.
- Sluice gates are the components that can offer precision in water flow in small-scale or large-scale projects.
Why Sluice Gates Are Essential?
Sluice gates can offer a wide variety of advantages that make them an absolute necessity in water management projects. Different benefits of sluice gates may include:
- Precise water flow control and management
- Flood mitigation
- Isolation for the maintenance and repair
- Easy to operate
- Low cost
- Easy and high maintainability
- Simple design and operation
- Durability and longevity
- Emergency water release
- Residue management
- Cost-effectiveness.
By offering precise control for water flow, sluice gates are becoming a highly advantageous and essential component required for modern water management.
People May Also Ask For – Sluice Gate? How It Works & Applications:
Question 1. What is the primary function of a sluice gate?
Answer. The main function of the sluice gate is to allow the controlled flow of water in different water reservoirs, including canals and rivers. These gates can act as movable barriers that can regulate the amount of water opening by raising or lowering. These gates can be used in different essential applications for the regulation of water supply to various areas, including agriculture, rivers, and canals.
Question 2. What is the working of a guide frame in sluice gates?
Answer. The guides on the sides of the gate frame can create a path through which the slide can travel when the gate is opened or closed. The gate frame can secure the flush bottom for the flow. A guide can prevent the leakage and provide moorage against the pressure.
Question 3. How can a sluice gate offer benefits in industrial applications?
Answer. Sluice gates can offer various benefits in industrial applications, including water management and controlling water levels. These gates can regulate the water flow, which can prevent flooding and ensure the appropriate water supply for the processes in the industries. These gates can be used to control the water flow in water treatment plants, wastewater treatment plants, and sewage treatment plants.
Question 4. What is the use of a sluice valve?
Answer. A sluice valve is a component of sluice gates and is also known as a gate valve. A sluice valve can be used to control the liquid flow in the pipeline, with complete opening or closing of the flow. This component can be used for complete on or off operation, but it cannot offer the precise regulation of fluid flow.